Neurological disorders have severe impacts on people’s lives in terms of both disability and dependency and have been linked to suicide. Yet, a comprehensive overview was lacking. This study examined whether people with specific neurological disorders die by suicide more often than other people. The study was based on the register data covering the entire population of Denmark during 1980-2016.
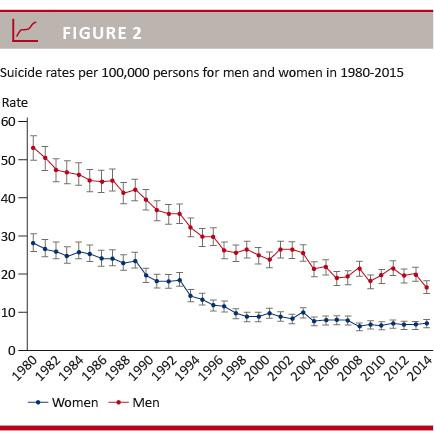
The findings from study, which was published in JAMA, shows that people with neurological disorders have a 75% higher suicide rate than people with no neurological disorders. Still, suicide deaths are rare events. While the suicide rate for the general population was around 20 per 100,000, the rate for people with neurological disorders is around 40 per 100,000 person-years. One out of 150 persons diagnosed with a neurological disorder dies by suicide. For severe neurological diseases, such as Huntington’s, one out of 61 diagnosed went on to die by suicide. This study is the most comprehensive assessment of neurological disorders’ link to suicide conducted to date.
The study shows that people who have been diagnosed with amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS) or Huntington’s disease have a particular high risks, as the suicide rate associated with these disorders is 4-5 times higher than in the general population. People who have been exposed to traumatic brain injury, multiple sclerosis, or epilepsy have a suicide rate, which is double the level of the one found among those with no such disorders.
People with dementia were found to have a 2-3 time higher suicide rate during the first three months after being diagnosed. On the other hand, people who had been diagnosed with dementia more than a year ago were found to have a lower suicide rate than the general population.
– This is the first time we have examined this many different neurological disorders to gain a more detailed understanding of when risk of suicide is pronounced. These insights can help us shape dedicated preventive effort says Dr. Annette Erlangsen, lead author and senior researcher at Danish Research Institute for Suicide Prevention (DRISP). The project has received support from the Psychiatric Research Foundation, Region of Southern Denmark.
Link to study:
https://jamanetwork.com/journals/jama/article-abstract/2760389
DRISP: Annette Erlangsen, Merete Nordentoft
Partners:
- Egon Stenager, Department of Neurology, Sønderborg, Hospital of Southern Jutland, Denmark
- Yeates Conwell, Center for the Study and Prevention of Suicide, University of Rochester Medical Center, USA
- Per Krag Andersen, Section of Biostatistics, University of Copenhagen, Denmark
- Keith Hawton, Centre for Suicide Research, University of Oxford, United Kingdom
- Michael Eriksen Benros, Research Unit, Mental Health Centre Copenhagen, Copenhagen, Denmark
- Elsebeth Stenager, Department of Regional Health Research, University of Southern Denmark, Odense, Denmark